
Beginning HTML and CSS
Class 3
Welcome!
Girl Develop It is here to provide affordable and accessible programs to learn software through mentorship and hands-on instruction.
Some "rules"
- We are here for you!
- Every question is important
- Help each other
- Have fun
What we'll be making today
Today we will be making a site from scratch using divs and spans to create a header, footer, sidebar and a content area.
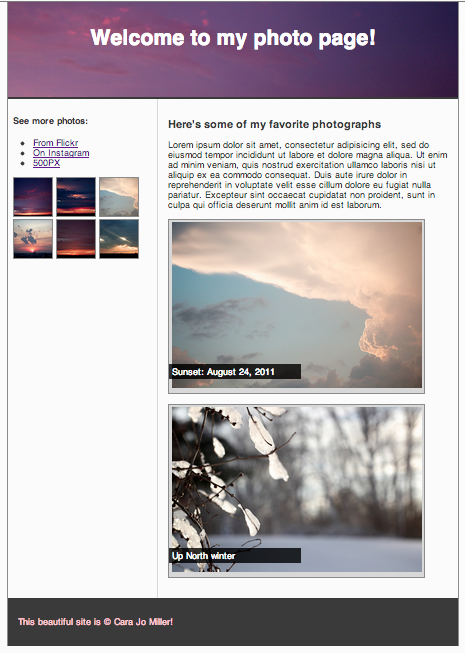
Inline vs Block
So far, we have mostly seen "block" elements
They appear on the next line, like paragraphs
There are also "inline" elements
They appear on the same line that they are written on.
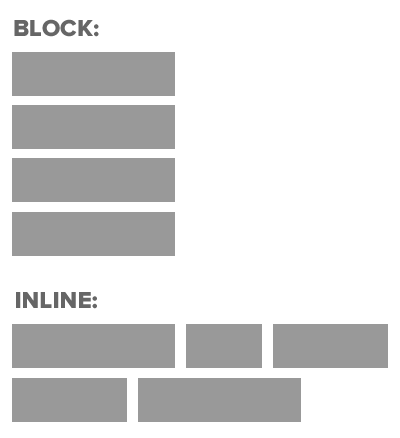
Block & Inline Elements,
- CSS divides HTML into two types: inline and block.
- After block elements, browsers render a new line.
- Inline elements: img, a, br, em, strong
- Block elements: p, h1, ul, li, almost everything else
Element: Div
- Block level element. Each new div is rendered on a new line.
- A division, or section of content within an HTML page.
- Used to group elements to format them with CSS.
- Apply IDs and Classes to divs to control their styles with CSS.
<div>
<p>Content</p>
<p>Content</p>
</div><div id="header">
<h1>Main Heading</h1>
</div><div class="sub-content">
<p>Some more content</p>
</div>Grouping elements with div
- The div tag is used everywhere to group elements together into sections.
- For example, what if we want the first 2 paragraphs of a section to be right-aligned, purple & bold, but we don't want any other paragraphs to be right-aligned?
- We would wrap them in a div element to style them differently.
Grouping elements with div, cont.
.align-right {
text-align:right;
color: green;
font-weight: bold;
}
<div class="align-right">
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit</p>
<p>Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore.</p>
</div>
<p>Magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam.</p>
<p>Quis nostrud exercitation ullamco.</a>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit
Sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore.
Magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam.
Quis nostrud exercitation ullamco.
Let's Develop It
Let's create a site using divs to separate content into different sections on our page.
Create a header, content area, sidebar, and a footer.
Element: Span
- Inline element. Each new span is rendered next to each other & only wraps when it reaches the edge of the containing element.
- Can be used to apply styles to text inline so as not to break the flow of content.
Span
Span is used to apply a specific style inline
.yellow {
color: yellow;
}
<p>Paragraph with <span class="yellow">yellow</span> text.</p>
Paragraph with yellow text.
Let's Develop It
Let's add some spans to our content to help highlight some text.
Pseudo-classes, more CSS for links
Changing the format of a link when you hover over it is accomplished by using pseudo-classes.
CSS pseudo-classes are used to add special effects to some selectors.
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
a:link {
text-decoration: none;
}
Pseudo-classes, more CSS for links
a:link { color: #FF0000; } /* unvisited link */
a:visited { color: #00FF00; } /* visited link */
a:hover { color: #FF00FF; } /* mouse over link */
a:active { color: #0000FF; } /* selected link */
Note: a:hover MUST come after a:link and a:visited in the CSS definition in order to be effective!
Note: a:active MUST come after a:hover in the CSS definition in order to be effective!
Let's Develop It
Add pseudo classes to your links
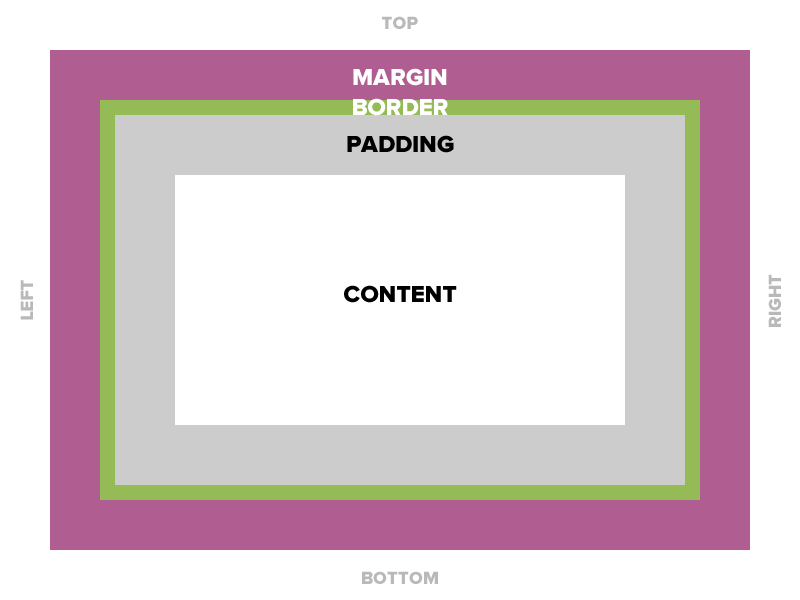
Box Model
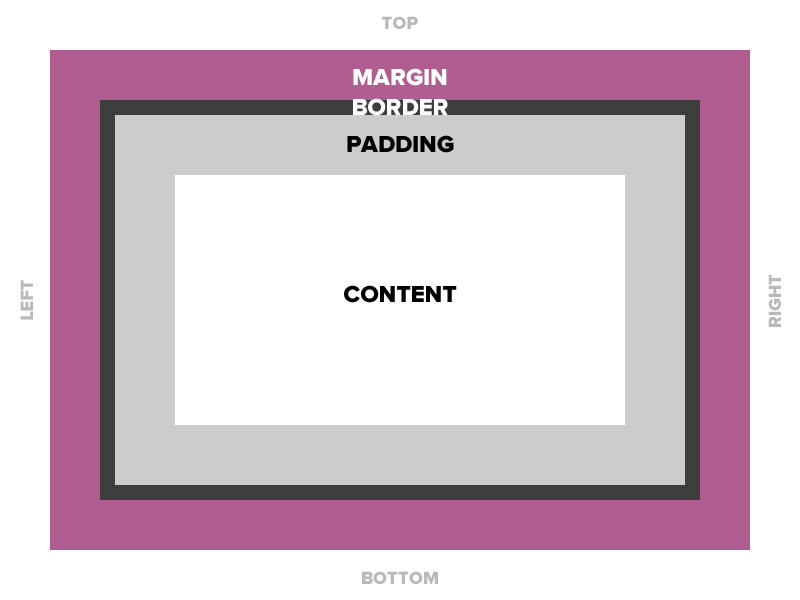
Padding
Space between the border and the content

Padding
Space between the border and the content
Adds to the total width of the box.
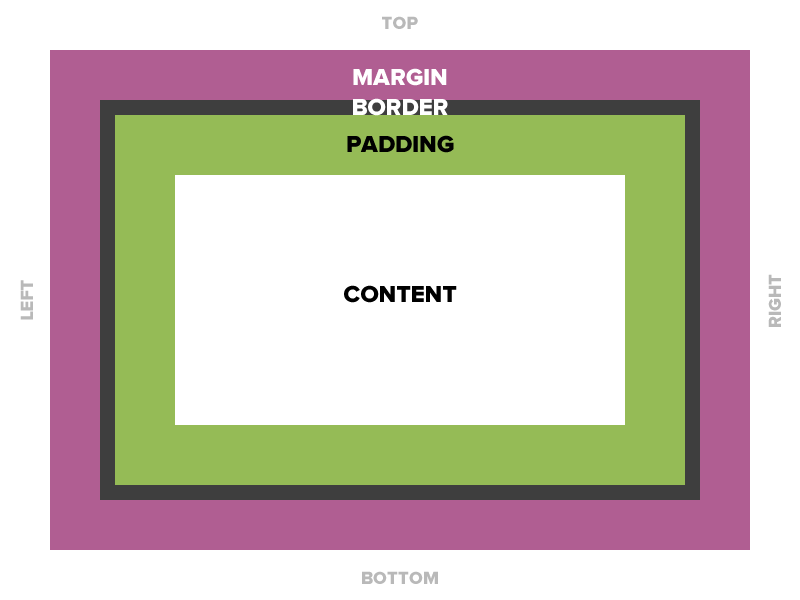
Padding
15 pixels on all sides
padding: 15px;
padding-top: 10px;
padding: 10px 5px 3px 5px;
Padding
Four values
padding: top right bottom left;
Two values
padding: top/bottom right/left;
One value
padding: all;
Padding
padding: 10px 20px 30px 40px;
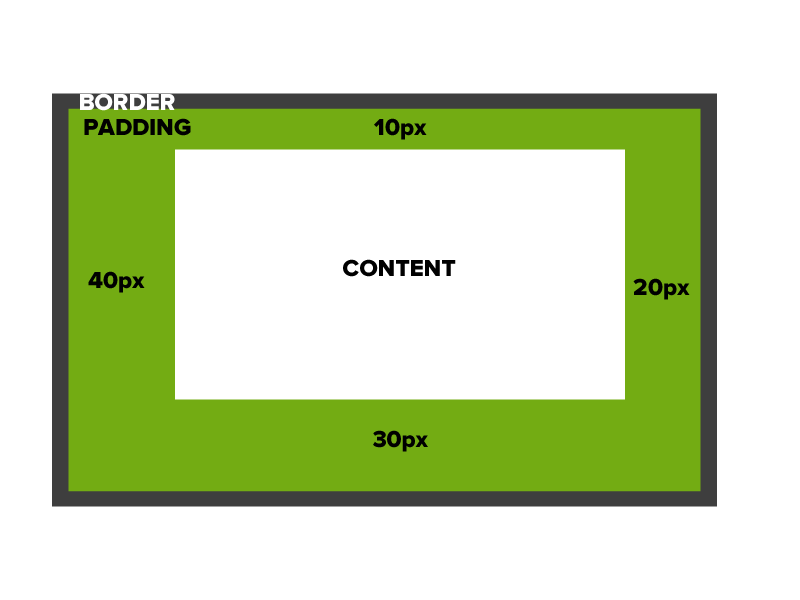
Border
The edge around the box, specified as "thickness, style, color."
Border
A solid red border
border: 1px solid #ff0000;
A thick dotted black top border
border-top: 4px dotted #000000;
Two different border styles
border-top: 1px solid #ff0000;
border-bottom: 4px dotted #000000;
Border - Other Properties
border-width: 10px;
border-style: dashed;
border-color: #666666;
You can specify each property separately, or all three together.
Margin
The transparent area around the box that separates it from other elements.

Margin
15 pixels on all sides
margin: 15px;
10 on top, 5 on right, 3 on bottom, 5 on left
margin: 10px 5px 3px 5px;
10 pixels on top
margin-top: 10px;
Auto Margin
If a margin is set to auto on a box that has width, it will take up as much space as possible.
CENTERED
margin: auto;
width: 300px;
FLUSH-RIGHT
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: 5px;
width: 300px;
Let's Develop it!
Let's add some padding, borders, and margins to our divs.
Let's center our entire document in the browser.
Property: Width
Sets the width of an element.
Does not include padding or borders, remember these add to the width.
Property: Height
Sets the height of an element.
Does not include padding or borders, remember these add to the width.
Let's develop it!
Add a width & height to our divs.
Use IDs to target each div with CSS